FOOD WASTEGE; CIRCULAR ECONOMY IS THE ANSWER
CIRCULAR ECONOMY
CIRCULAR ECONOMY
- A circular economy mimics natural systems, ensuring that waste doesn't exist but instead becomes feedstock for another cycle.
- Organic resources, such as food by-products, are transformed into valuable inputs rather than discarded.
- Innovations in this space aim to reduce waste, promote sustainability, and create a healthier food system.
Those practices repurposes ingredients that would otherwise go to waste.
It aligns with life cycle thinking and fosters a circular food economy.
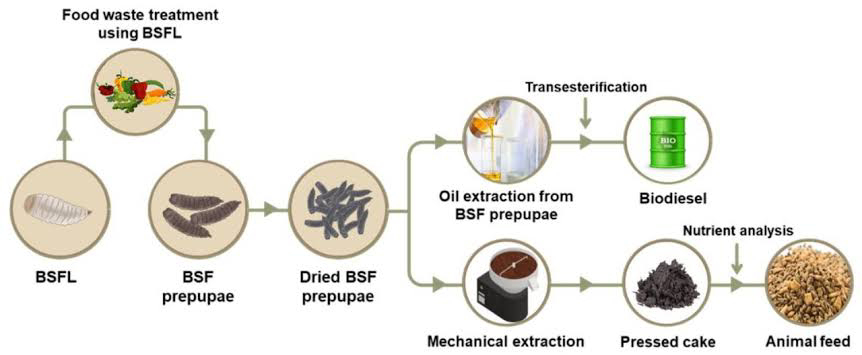
- The black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) is a medium-sized, predominantly black-colored fly.
- It devours organic waste and converts it into compost or uses its larvae as animal feed.
- In many countries, BSF larvae are now seen as an alternative protein source for chickens.
- The larvae feed on the waste, rapidly digesting it and transforming it into high-protein biomass.
- BSF farming offers a sustainable way to address waste and enhance protein availability.
Meat and Bone Meal (MBM)
- MBM is a byproduct of meat processing.
- It contains nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P), making it a balanced and fast-acting nutrient source for soil.
- Together with other organic materials (such as bone meal, blood meal, and feather meal), MBM enriches soil and promotes plant growth.
- Coffee grounds, rich in nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorus, make excellent slow-release fertilizers.
- Bananas, loaded with potassium, magnesium, and vitamins, can benefit your garden when used as fertilizer.
Remember, these practices contribute to a more sustainable and efficient food system, reducing waste and nourishing our planet.
About the write
Kindly follow







Comments
Post a Comment